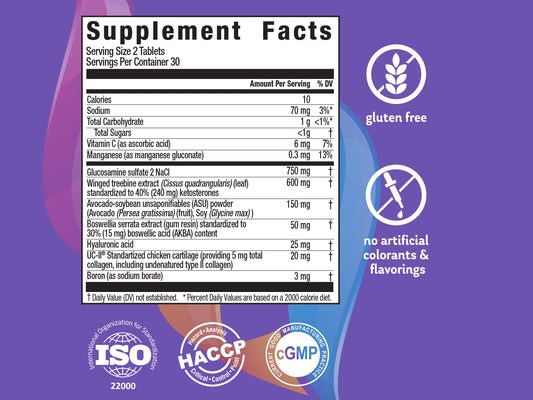
Glucosamine is a building block for articular cartilage, naturally sugar-synthesized from glucose by the major cells of the cartilage called chondrocytes.
Glucosamine is used to produce larger molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAG) and proteoglycans, which are the main constituent of the cartilage matrix. Together with its metabolites, it plays essential role as a source of building material for tendons and ligaments1-4.* Glucosamine is also needed for the synthesis of hyaluronic acid, an essential component of the joint fluid that help maintain its viscosity and lubricating properties5,3.*
Though technically a type of sugar, Glucosamine doesn't appear to affect blood sugar levels or insulin sensitivity6.* There are several forms of glucosamine, including glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine hydrochloride and N-acetyl glucosamine. These forms aren't considered interchangeable. Until now, glucosamine sulfate has been most thoroughly researched by scientists who found its positive effects on healthy joint structure and function1,7.*
- Noyszewski EA, Wroblewski K, Dodge GR, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(5):1089-1095. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200105)44:5<1089::AID-ANR189>3.0.CO;2-9
- Devirian TA, Volpe SL. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2003;43(2):219-231. doi:10.1080/10408690390826491
- Gandhi NS, Mancera RL. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008;72(6):455-482. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00741.x
- Igarashi M, Sakamoto K, Nagaoka I. Int J Mol Med. 2011;28(3):373-379. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2011.686
- Henrotin Y, Chevalier X, Herrero-Beaumont G, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2013;6:115. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-6-115
- Simon RR, Marks V, Leeds AR, Anderson JW. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011;27(1). doi:10.1002/dmrr.1150
- Akmal M, Singh A, Anand A, et al. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(8):1143-1149. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.87B8.15083